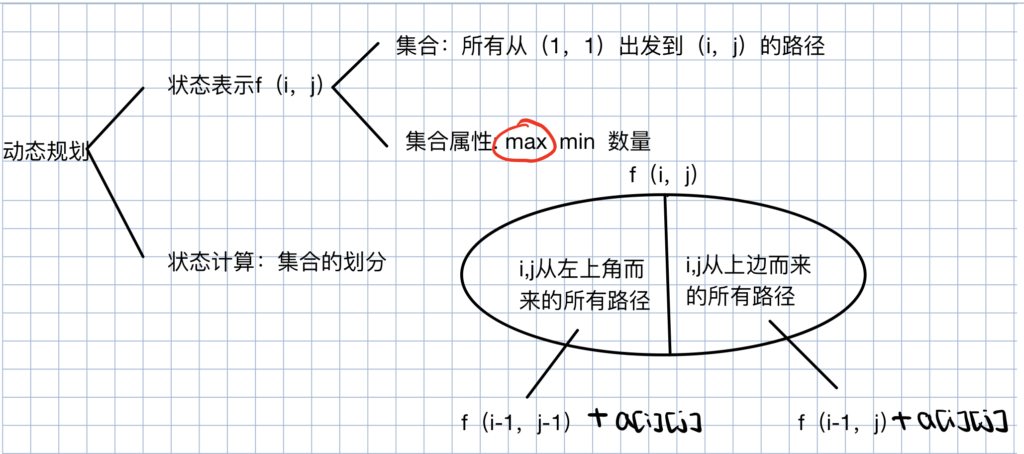
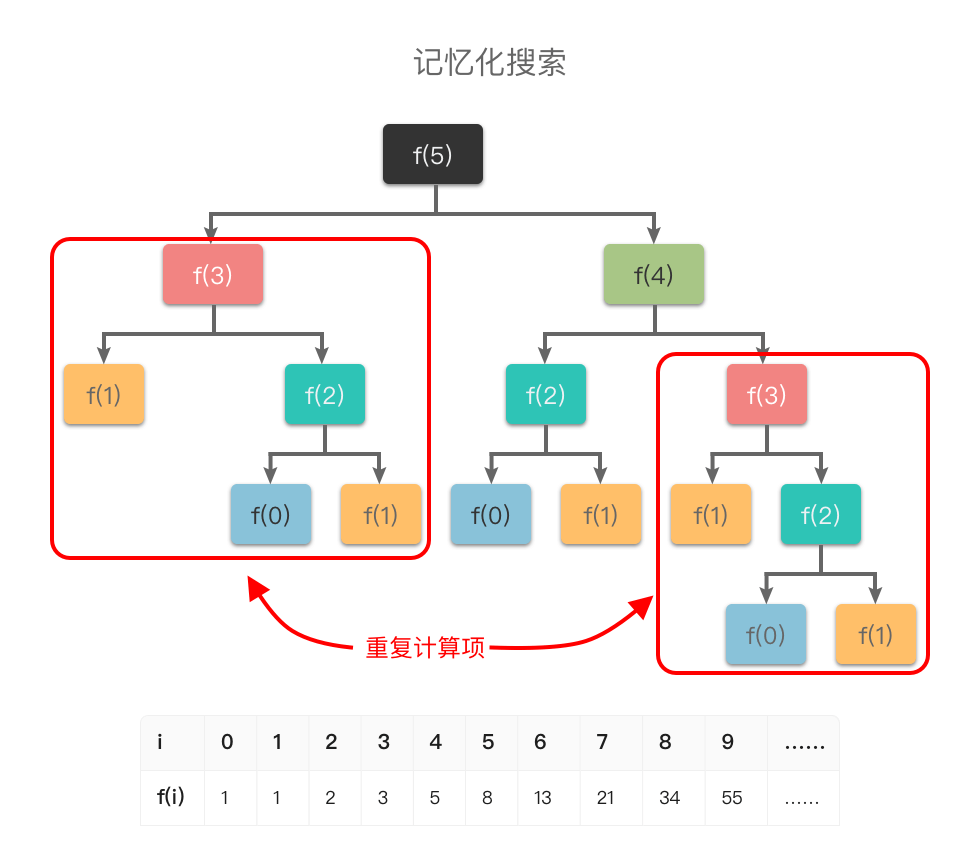
基本概念
二叉树由结点的有限集合构成。
这个有限集合要么是空集,要么是一个根节点及两棵互不相交、分别称为这个跟的左子树和右子树的二叉树组成的集合。
二叉树的特点
每个结点最多有两棵子树,所以二叉树中不存在度大于2的结点。
左子树和右子树是有顺序的,次序不能随意颠倒。
及时树中某结点只有一颗子树,也要区分它是左子树还是右子树。
二叉树的五种基本形态
- 空
- 只有一个根节点
- 根节点只有左子树
- 根节点只有右子树
- 根节点既有左子树,又有右子树
相关概念
- 边(edge):两个结点(node)的有序对(order pair),称为边
- 结点的度:一个节点含有的子树的个数成为该结点的度
- 叶节点:度为0的结点成为叶节点
- 路径(path):根节点到某个子节点的”路“
- 路径长度(the length of the paths):根节点到某个子节点的”路“的长度
- 层数:根是第0层(其他结点的层数等于其父节点的层数加1)
- 深度:层数最大的叶节点的层数
二叉树的性质
- 在二叉树中,第i层上最多有2i个节点(i≥0)
- 深度为k的二叉树最多有2k+1-1个节点(k≥0),其中深度的定义(depth)为二叉树层数最大的叶节点的层数
- 一颗二叉树,若其终端节点数为n0,度为2的节点数为n2,则n0=n2+1
- 满二叉树性质:非空满二叉树树叶数目等于其分支节点数+1
- 满二叉树性质推论:一个非空二叉树的空子树数目等于其节点数+1
- 有n个节点(n>0)的完全二叉树的高度为log2(n+1),深度为log2(n+1)-1
二叉树的遍历
1.前序遍历:先根 再左 再右
规则:若二叉树为空,则操作返回,否则,先访问根节点,然后前序访问左子树,之后前序访问右子树。
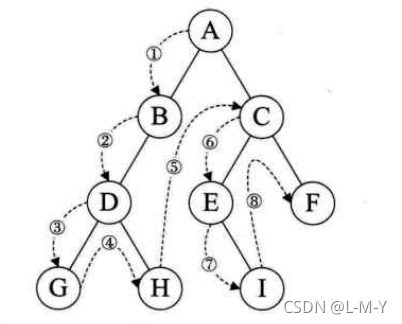
代码模版:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int data;//节点
int left;//左子树
int right;//右子树
}a[30];
void preorder(int x){//先序遍历
if(x==0)return;
cout<<a[x].data;
preorder(a[x].left);
preorder(a[x].right);
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i].data>>a[i].left>>a[i].right;
preorder(1);
cout<<endl;
}2.中序遍历:先左 再根 再右
按中序遍历左子树,访问根节点,然后按中序遍历右子树。

代码模版:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int data;//节点
int left;//左子树
int right;//右子树
}a[30];
void inorder(int x){//中序遍历
if(x==0)return;
inorder(a[x].left);
cout<<a[x].data;
inorder(a[x].right);
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i].data>>a[i].left>>a[i].right;
preorder(1);
cout<<endl;
inorder(1);
cout<<endl;
postorder(1);
}3.后序遍历:先左 再右 再根

按后序遍历左子树,按后序遍历右子树,然后访问根节点。
代码模版:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int data;//节点
int left;//左子树
int right;//右子树
}a[30];
void postorder(int x){//后序遍历
if(x==0)return;
postorder(a[x].left);
postorder(a[x].right);
cout<<a[x].data;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i].data>>a[i].left>>a[i].right;
preorder(1);
cout<<endl;
inorder(1);
cout<<endl;
postorder(1);
}这个根,指的是每个分叉子树(左右子树的根节点)根节点并不只是整棵树的根节点
附件:
参考资料: